Introduction
In today’s fast-paced software world, building scalable, flexible, and maintainable applications is more important than ever. Traditional monolithic applications are often heavy, difficult to manage, and slow to update. That’s where microservices architecture comes in. By breaking applications into smaller, independent services, organizations can develop, deploy, and scale faster. But building microservices isn’t as simple as splitting code into pieces. You need proven strategies to design them effectively, which is where microservices design patterns come into play.
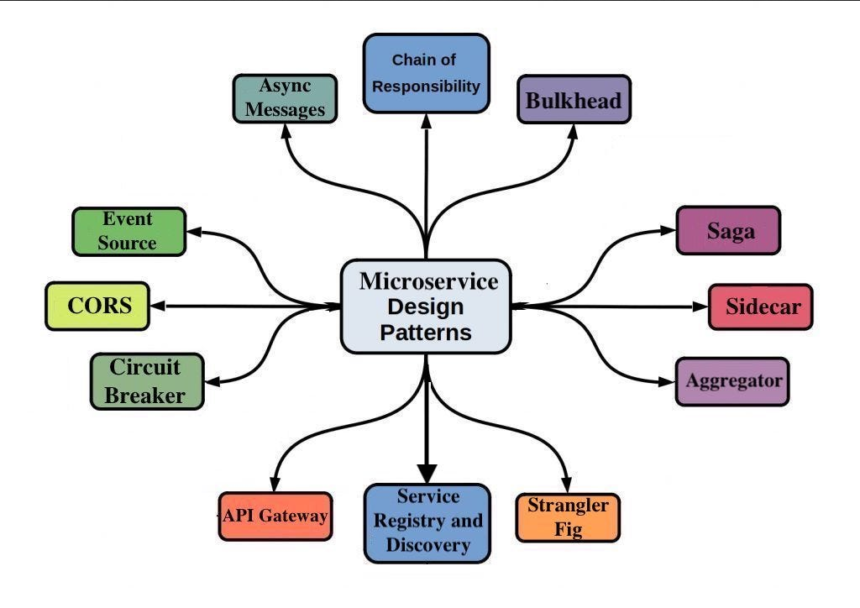
These design patterns are tried-and-tested solutions for common problems in microservices development. They guide developers on structuring services, managing communication, handling data, and ensuring resilience. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, understanding these patterns can save time, reduce errors, and improve the overall quality of your applications. In this article, we’ll explore the most important microservices design patterns, real-world examples, and practical tips to implement them successfully.
1. What Are Microservices Design Patterns?
Simply put, microservices design patterns are reusable solutions for designing, building, and managing microservices. They solve common problems like service communication, data consistency, and failure handling. Think of them as blueprints: rather than inventing your own approach each time, you can rely on these patterns to guide you.
For example, if you need one service to call another safely, a design pattern provides a structured way to do it without breaking the system. These patterns are categorized based on functionality some focus on service communication, others on scalability, security, or resilience. Using these patterns makes your microservices architecture more robust, predictable, and easier to maintain.
2. Benefits of Using Microservices Design Patterns
Adopting microservices design patterns brings several benefits:
- Scalability: Services can scale independently without affecting others.
- Resilience: Systems handle failures gracefully, reducing downtime.
- Maintainability: Smaller, modular services are easier to understand and update.
- Faster Development: Developers can reuse proven patterns instead of reinventing solutions.
- Better Collaboration: Teams can work on separate services without conflicts.
For instance, Netflix, a pioneer in microservices, relies heavily on patterns to manage thousands of services running globally. Without them, achieving such reliability and scalability would be nearly impossible.
3. Decomposition Patterns
The first step in building microservices is deciding how to break down a monolithic application. Decomposition patterns provide strategies for dividing an application into microservices.
- Decompose by Business Capability: Organize services around business functions. For example, in an e-commerce app, you could have separate services for payments, inventory, and orders.
- Decompose by Subdomain: Based on Domain-Driven Design, each subdomain of the business has its own service. This pattern works well for complex systems with multiple domains.
By following these patterns, you ensure that services remain focused, loosely coupled, and independently deployable.
4. Integration Patterns
Once services are split, they need to communicate. Integration patterns solve this challenge.
- API Gateway Pattern: Acts as a single entry point for all client requests, routing them to the appropriate services. It also handles authentication, logging, and caching.
- Aggregator Pattern: Combines responses from multiple services into a single response for the client. This reduces the client’s complexity.
- Proxy Pattern: Intercepts calls to services, providing additional functionality like load balancing or monitoring.
These patterns help maintain efficiency and consistency in inter-service communication, especially in large, distributed systems.
5. Database Patterns
Data management is a critical concern in microservices. Each service should ideally own its own database, but this can create challenges. Database patterns address these issues:
- Database per Service: Each service has a dedicated database, reducing dependency conflicts.
- Shared Database: Multiple services use a single database. Though simpler, it increases coupling and requires careful schema management.
- CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation): Separates read and write operations for better performance. Writes go to one model, and reads go to another.
Choosing the right pattern ensures data consistency while maintaining service independence.
6. Observability Patterns
Microservices often involve dozens or hundreds of services. Monitoring and debugging such systems can be challenging. Observability patterns help developers track performance and detect issues early.
- Log Aggregation: Collect logs from all services in a central system for easier analysis.
- Distributed Tracing: Tracks a request across multiple services to identify bottlenecks.
- Health Check API: Allows services to report their status, enabling automated monitoring and alerting.
These patterns are crucial for maintaining reliability and preventing small issues from escalating into system-wide failures.
7. Resiliency Patterns
Microservices must be resilient because failures are inevitable. Resiliency patterns ensure that your system continues functioning smoothly even when problems occur.
- Circuit Breaker Pattern: Stops calls to a failing service to prevent cascading failures.
- Retry Pattern: Automatically retries failed requests to handle temporary errors.
- Bulkhead Pattern: Isolates services or resources to prevent a single failure from affecting others.
Netflix, Amazon, and other cloud giants use these patterns extensively to deliver high-availability services.
8. Security Patterns
Security is a critical concern in microservices, especially with distributed services exposing multiple endpoints. Security patterns help safeguard your applications:
- Token-Based Authentication: Use JWT tokens to authenticate users across multiple services.
- OAuth2 / OpenID Connect: Secure API access using standardized protocols.
- Service Mesh Security: Encrypt communication between services automatically using TLS.
Implementing these patterns ensures that your microservices are protected from unauthorized access and data breaches.
9. Deployment Patterns
Deploying microservices efficiently is vital for continuous delivery. Deployment patterns provide guidance:
- Blue-Green Deployment: Deploy new versions alongside old ones to reduce downtime.
- Canary Deployment: Roll out updates gradually to a subset of users before full deployment.
- Rolling Deployment: Update services in small increments to prevent system-wide failures.
These patterns minimize disruption and make updates safer, even in large-scale systems.
10. Event-Driven Patterns
Event-driven microservices communicate through events rather than direct calls. Event-driven patterns improve scalability and decoupling:
- Event Sourcing: Stores state changes as a sequence of events, enabling better auditing and recovery.
- Publish-Subscribe Pattern: Services publish events to a broker, and subscribers react independently.
- Event Notification: Services notify others of changes, triggering asynchronous workflows.
These patterns enhance system responsiveness and reduce tight coupling between services.
11. Testing Patterns
Testing microservices is tricky due to their distributed nature. Testing patterns make it manageable:
- Consumer-Driven Contracts: Ensure that service contracts meet consumer expectations.
- Test Isolation: Test each service independently to prevent interference.
- End-to-End Testing: Verify the entire workflow across multiple services.
Using these patterns ensures your microservices work correctly individually and as part of a larger system.
12. Real-World Example: E-Commerce Microservices
Imagine an online store:
- Order Service: Handles order creation and updates.
- Payment Service: Processes payments securely.
- Inventory Service: Manages stock availability.
- Notification Service: Sends emails and alerts.
Using microservices design patterns:
- API Gateway manages requests from users.
- Circuit Breaker protects payment failures from affecting orders.
- Event Sourcing keeps track of all inventory changes.
- CQRS improves performance by separating order read and write operations.
This modular approach makes the system more scalable, resilient, and easier to maintain.
FAQs About Microservices Design Patterns
1. What is the main purpose of microservices design patterns?
They provide proven solutions to common problems in microservices development, making systems scalable and resilient.
2. How do microservices differ from monolithic architecture?
Microservices are modular and independently deployable, while monoliths are single, tightly coupled applications.
3. Which design pattern is best for service communication?
API Gateway, Aggregator, and Event-Driven patterns are commonly used for efficient communication.
4. How does CQRS improve performance?
CQRS separates read and write operations, allowing optimized queries for faster response times.
5. Can microservices design patterns prevent failures?
They can’t prevent failures entirely but increase system resilience and fault tolerance.
6. Are these patterns suitable for small applications?
Yes, but they are most beneficial for large, complex, or scalable systems.
Conclusion
Microservices design patterns are not just theory they are practical tools that help developers build scalable, resilient, and maintainable systems. By understanding and applying patterns for decomposition, integration, data management, security, and resiliency, you can reduce complexity and speed up development.
Whether you’re working on an e-commerce platform, a fintech application, or a cloud service, these patterns guide you toward best practices, avoiding common pitfalls. Start small, experiment with patterns that fit your needs, and gradually expand your architecture.